This form is characterized by a fulminant and progressive inflammation with progressive change of some other symptoms. For acute periodontitis is characterized by severe localized pain permanent. The intensity of pain depends on the redness, swelling, the number and nature of exudate. Initially, acute periodontitis indicated mild severe aching pain, which is usually localized and corresponds to the area of the damaged tooth. Later, the pain becomes more intense, tearing and throbbing, sometimes radiating along the branches of the trigeminal nerve, which according to some authors suggest a transition in purulent inflammation.
Duration of the acute apical process lasts 2-3 days. up to 2 weeks, and the initial forms of inflammation are very different from those expressed forms and require different approaches regarding the management of their treatment. To better understand the clinical and pathological anatomy of acute apical periodontitis, arbitrarily singled out two mutually related and derived from a different stage or phase.
First phase. The first phase of intoxication observed periodontal inflammation in early and often after a late or incorrect treatment of pulpitis. Its characteristic is the appearance of long, uninterrupted pain aching nature. Sometimes attached to this increased sensitivity for bite on the aching tooth. On the gums of the tooth unchanged inflammatory nature of this period there, and percussion in a vertical direction, there may be increased sensitivity of periodontal. Regional lymph nodes may be enlarged.
In the formation of an abscess may be a fluctuation of fluid under the thinned layer of mucous membrane of the gums. In the case of breaking and formation of pus on the gums or fistula of the facial skin tissue decreases stress and pain becomes less intense.
oxidative edema. In this phase, the predominant perivascular lympho-histiocytic infiltrates and with a mixture of single polynuclear.
Second phase. This phase is characterized by a pronounced exudative process continuous pain. Last stay on the same level or increase. There is tenderness to bite on the tooth, often painfully, even a light touch to the aching tooth. Percussion of the tooth in this period of sharply painful at first only in the vertical, and then in either direction. The accumulation of fluid in the apical area teriodonta and dysfunction of the pressure distribution cause the patient a sense of elongation of the tooth, as well as its pathological mobility. Last due to a violation of anatomical features of periodontal due to infiltration, and partial destruction fibrotic (collagen) fibers. Gums of the patient teeth often hyperemic and edematous, palpation of the transition fold, respectively, the apex of the root pulp painful teeth, usually necrotic, so the tooth does not respond to temperature nor to electric stimuli.
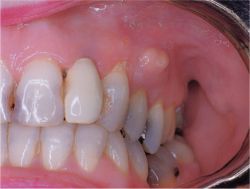
In some cases, significant collateral tissue swelling admaxillary. The transition is smoothed as a result of fold formation inflammatory infiltrate or abscess. Percussion of the tooth may be in these cases is not very painful, but is sharply painful palpation of the transitional fold.
From the roots of premolars and molars of the maxilla abscess can go to the maxillary sinus and cause its inflammation. Common symptoms in the form of a sharp rise in temperature and chill, with rare exceptions, are absent, due to rapid absorption and neutralization of toxic products in the regional lymph nodes. But sometimes the patient may show leukocytosis (up to 15-25 - 109 / L) and increased ESR. An objective examination can establish an increase in morbidity and submandibular, and sometimes the chin lymph nodes on the side of the sick tooth.
Duration of the acute apical process lasts 2-3 days. up to 2 weeks, and the initial forms of inflammation are very different from those expressed forms and require different approaches regarding the management of their treatment. To better understand the clinical and pathological anatomy of acute apical periodontitis, arbitrarily singled out two mutually related and derived from a different stage or phase.
First phase. The first phase of intoxication observed periodontal inflammation in early and often after a late or incorrect treatment of pulpitis. Its characteristic is the appearance of long, uninterrupted pain aching nature. Sometimes attached to this increased sensitivity for bite on the aching tooth. On the gums of the tooth unchanged inflammatory nature of this period there, and percussion in a vertical direction, there may be increased sensitivity of periodontal. Regional lymph nodes may be enlarged.
In the formation of an abscess may be a fluctuation of fluid under the thinned layer of mucous membrane of the gums. In the case of breaking and formation of pus on the gums or fistula of the facial skin tissue decreases stress and pain becomes less intense.
oxidative edema. In this phase, the predominant perivascular lympho-histiocytic infiltrates and with a mixture of single polynuclear.
Second phase. This phase is characterized by a pronounced exudative process continuous pain. Last stay on the same level or increase. There is tenderness to bite on the tooth, often painfully, even a light touch to the aching tooth. Percussion of the tooth in this period of sharply painful at first only in the vertical, and then in either direction. The accumulation of fluid in the apical area teriodonta and dysfunction of the pressure distribution cause the patient a sense of elongation of the tooth, as well as its pathological mobility. Last due to a violation of anatomical features of periodontal due to infiltration, and partial destruction fibrotic (collagen) fibers. Gums of the patient teeth often hyperemic and edematous, palpation of the transition fold, respectively, the apex of the root pulp painful teeth, usually necrotic, so the tooth does not respond to temperature nor to electric stimuli.
In some cases, significant collateral tissue swelling admaxillary. The transition is smoothed as a result of fold formation inflammatory infiltrate or abscess. Percussion of the tooth may be in these cases is not very painful, but is sharply painful palpation of the transitional fold.
From the roots of premolars and molars of the maxilla abscess can go to the maxillary sinus and cause its inflammation. Common symptoms in the form of a sharp rise in temperature and chill, with rare exceptions, are absent, due to rapid absorption and neutralization of toxic products in the regional lymph nodes. But sometimes the patient may show leukocytosis (up to 15-25 - 109 / L) and increased ESR. An objective examination can establish an increase in morbidity and submandibular, and sometimes the chin lymph nodes on the side of the sick tooth.

No comments:
Post a Comment